2. The content workflow
Like development and design, content has a defined workflow, which tells cross-functional stakeholders where content is in the whole process and clarifies what each of them must do to facilitate what’s needed and when it’s needed. It also helps the project manager recognize bottlenecks so that she can take measures to keep content moving toward production.
To better understand a content workflow, we’ll analyze the role and responsibilities of a content strategist in an end-to-end production cycle: pre-production production post-production. As designers, this will help you understand the different ways you can leverage content strategy, the different stages you can collaborate, or the systematic process you could follow if content strategy falls to you.
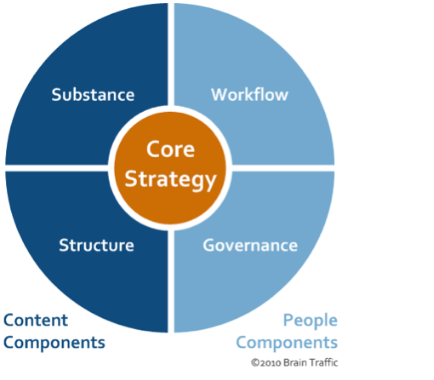
Let’s start with a look at the four components of content strategy, as delineated by Brain Traffic’s Melissa Rach, in her widely cited Content Strategy Quadrant. At the center is the core content strategy, the approach you’ll take with your website, product, or service content to meet user needs and achieve your business goals. Four broad components need to work in sync for that strategy to be effective:
|
Content components Substance refers to the message, voice, and types of content. Structure involves decisions regarding the technology, taxonomy, terminology and structure for a site or app. People components Workflow involves the processes and tools a content team will use to create, edit, maintain, and archive content, and ensure that it appears to the right people at the right time. Governance is closely connected with workflow and refers to the hierarchy of decision makers as well as the communication structure within the team. |
A content strategist typically comes into a UX project during the Discovery or Research phase. Their work continues nearly through to the end of the project. So, in that respect, an end-to-end content lifecycle corresponds with an end-to-end project lifecycle, which includes pre-production; production and post-production.